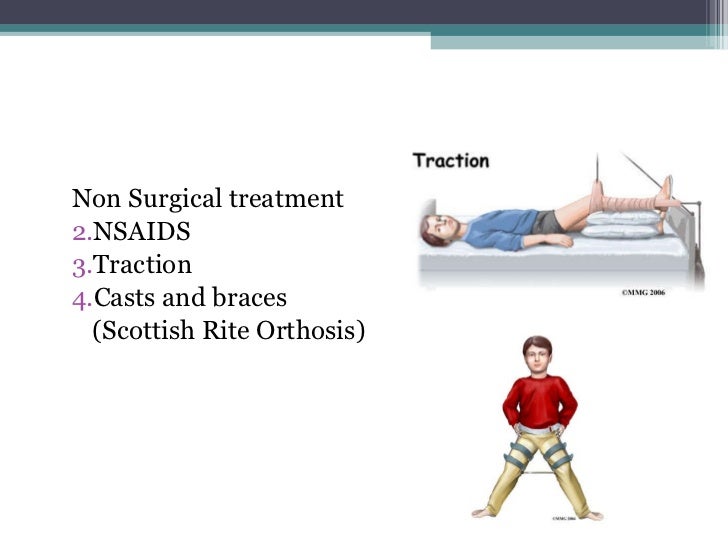
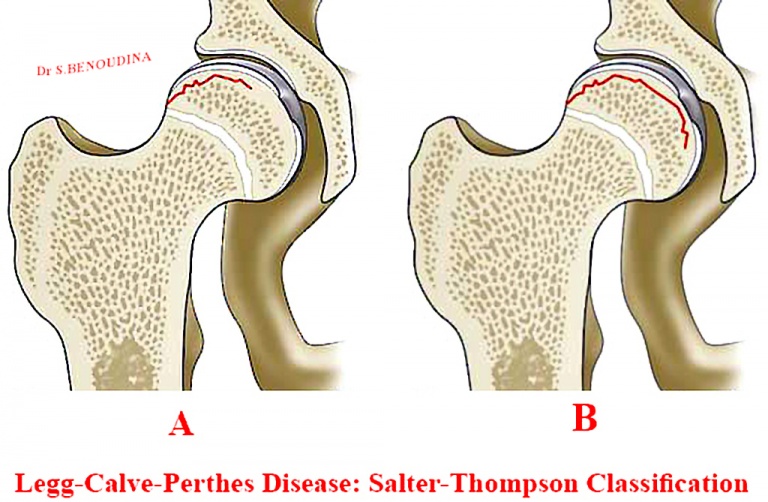
Treatment For Legg Calve Perthes Disease
Treatment for legg calve perthes disease. Patients without excessive lateral extrusion or other signs of head at risk and half or more of the femoral head involved probably can be treated for short periods of time in an. Removal of loose bodies and debridement of cartilage flaps provide most of the therapeutic benefit. Surgical Treatment for Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease in Children Surgery for Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease also called Perthes disease is usually reserved for children ages seven and older whose symptoms are less likely to be managed effectively by physical therapy or a cast.
According to two recent multicenter prospective cohort studies current nonoperative and operative treatments have modest success rates of producing a good outcome with a spherical femoral head in older children with Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. There is no clear consensus on nonoperative or operative treatment protocols for pediatric patients presenting with LCPD. Your veterinarian will perform a femoral head and neck excision.
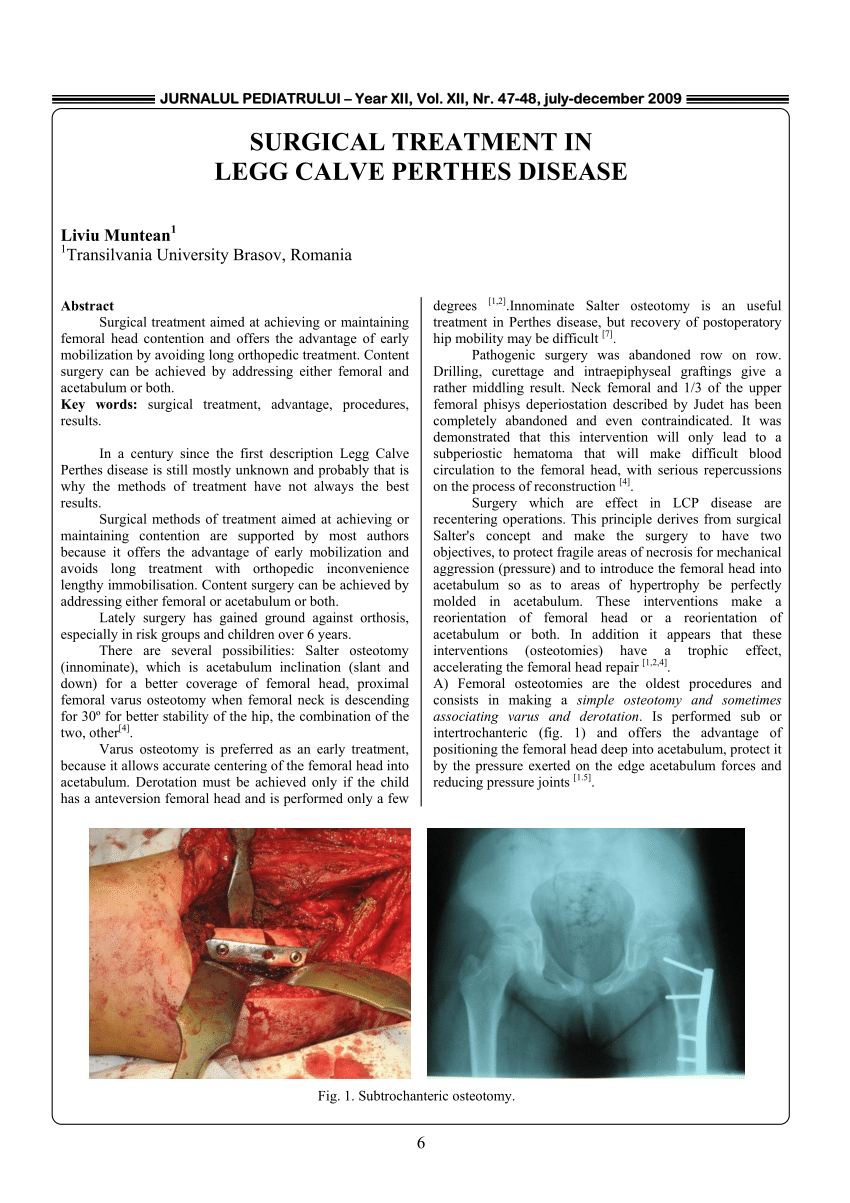
Salter applied this treatment to LCPD to surgically contain the femoral head when extrusion was present 60. In this type of procedure the bone is cut and repositioned to keep the femoral head snug within the acetabulum. Containment and surgical treatment supports the concept that containment is a key factor in the treatment of Legg-Perthes disease.
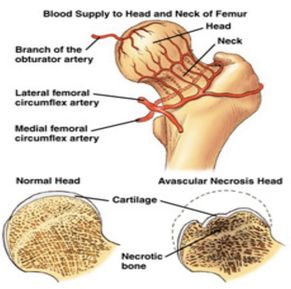
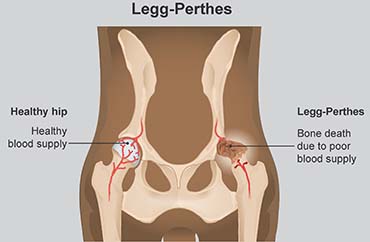
Physiotherapy using muscle strengthening and stretching exercises is claimed to have beneficial effects in the treatment of Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease is a juvenile form of idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head that can lead to permanent femoral head deformity and premature osteoarthritis. Up to now different surgical and nonsurgical treatments including femoral varus osteotomy innominate osteotomy pelvic osteotomies triple osteotomy Chiari osteotomy and shelf acetabuloplasty have been suggested for noncontainable LCPD hips.
All treatment options for Perthes disease try to position and hold the hip in the acetabulum as much as possible. However no scientific evidence is available concerning effectiveness of treatment. We conclude that arthrodiastasis using an external fixator can be a relatively promising surgical procedure for the treatment of late-onset Legg-Calve-Perthes disease.
The most common surgical procedure for treating Perthes disease is an osteotomy. Salters innominate osteotomy was initially developed for the treatment of congenital hip dislocations 59. The socket works like a mold for the fractured femoral head during the healing process.
Many children who are diagnosed with Perthes disease do not require any treatment except careful watching. Hip arthroscopy has been shown to be therapeutic for patients with Legg Calve Perthes disease.
This was analogous to treating a dysplastic hip with residual subluxation.
We conclude that arthrodiastasis using an external fixator can be a relatively promising surgical procedure for the treatment of late-onset Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. Physiotherapy using muscle strengthening and stretching exercises is claimed to have beneficial effects in the treatment of Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. This involves the removal of the disintegrating bone on the ball portion of. The most common surgical procedure for treating Perthes disease is an osteotomy. This study uses meta-analysis and a binary logistic regression. The socket works like a mold for the fractured femoral head during the healing process. Removal of loose bodies and debridement of cartilage flaps provide most of the therapeutic benefit. All treatment options for Perthes disease try to position and hold the hip in the acetabulum as much as possible. Up to now different surgical and nonsurgical treatments including femoral varus osteotomy innominate osteotomy pelvic osteotomies triple osteotomy Chiari osteotomy and shelf acetabuloplasty have been suggested for noncontainable LCPD hips.
Physiotherapy using muscle strengthening and stretching exercises is claimed to have beneficial effects in the treatment of Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. In this type of procedure the bone is cut and repositioned to keep the femoral head snug within the acetabulum. However no scientific evidence is available concerning effectiveness of treatment. According to two recent multicenter prospective cohort studies current nonoperative and operative treatments have modest success rates of producing a good outcome with a spherical femoral head in older children with Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. Treatment of Late-Onset Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease by Arthrodiastasis. This alignment is kept in place with screws and plates which will be. Hip arthroscopy has been shown to be therapeutic for patients with Legg Calve Perthes disease.



/perthes-disease-4174322_FINAL-5c05c1c546e0fb0001f4a111.png)
































Post a Comment for "Treatment For Legg Calve Perthes Disease"