Coronary Heart Disease Risk Equivalent
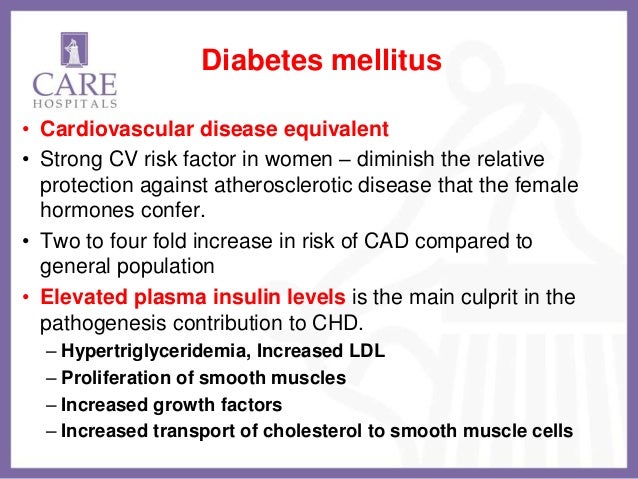
Coronary heart disease risk equivalent. The purpose of our study was to confirm or refute the view that diabetes be regarded as a coronary heart disease CHD risk equivalent and to test for sex differences in mortality. The concept of diabetes as a coronary heart risk CHD equivalent postulates that patients with diabetes who do not yet have CHD are at an equally high cardiovascular risk as non-diabetic patients with CHD. In type 2 diabetic women the relative risk is even greater 2.
A womans risk of death from CAD is equal to or greater than the same risk for a man by age 75. These arteries supply your heart muscle with oxygen-rich blood. This implies important therapeutic psychological and economical consequences.
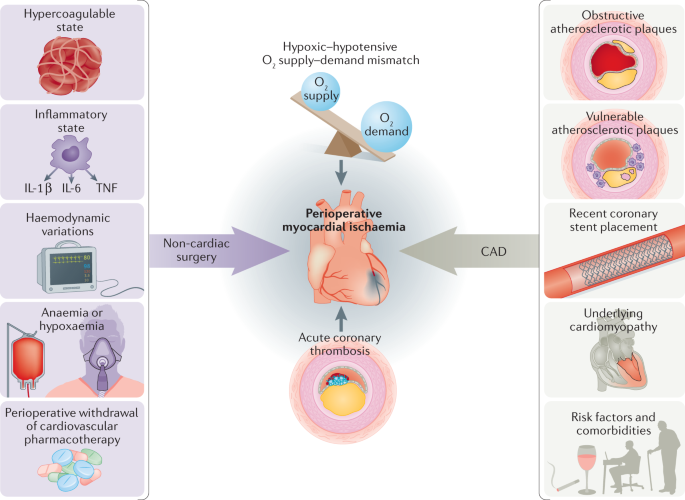
Treatments used for management of established CAD might have similar benefits for patients with concomitant CKD. Screening of 44052 electronic medical records from a primary care practice identified 1512 high-risk patients with documented coronary heart disease CHD or CHD risk equivalents. Some degree of cardiovascular disease at the level of the heart muscle and coronary arteries often.
Plaque is made up of fat cholesterol calcium and. Should CKD be a coronary heart disease risk equivalent. The calculator reflects new guidelines and updates by the National Institutes of Health in December 2015.
CHD occurs when plaque builds up inside the coronary arteries. However whereas several reports support the concept of. This calculator will determine your risk of developing coronary heart disease over the next 10 years and compare this to the risk of others of the same age.
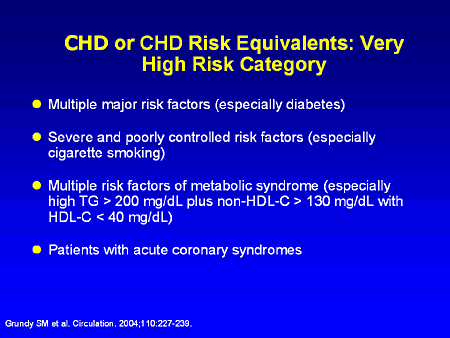
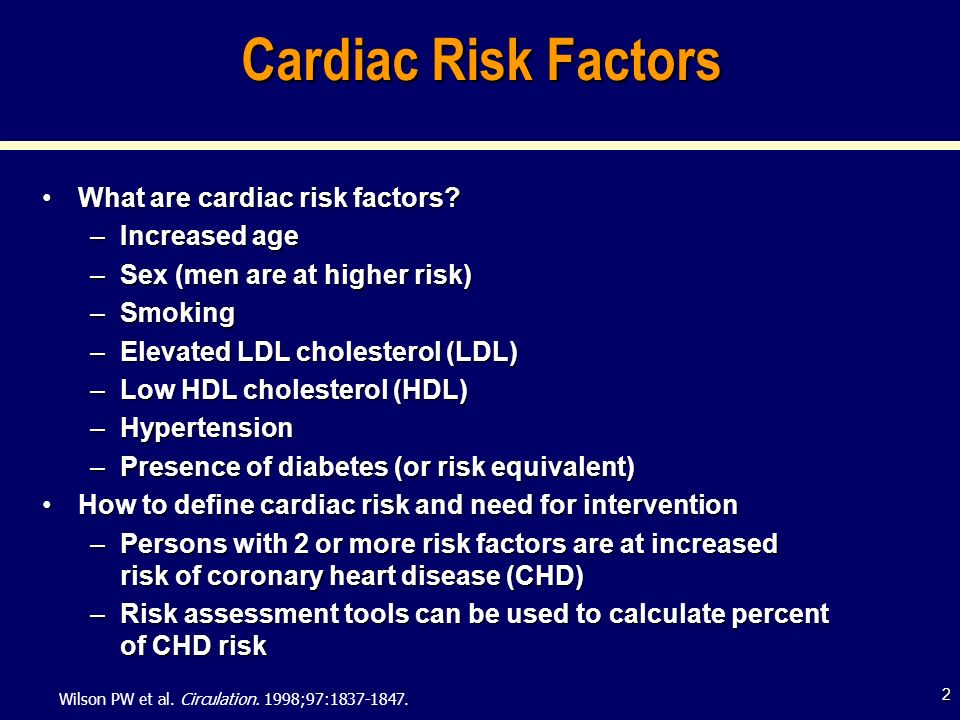
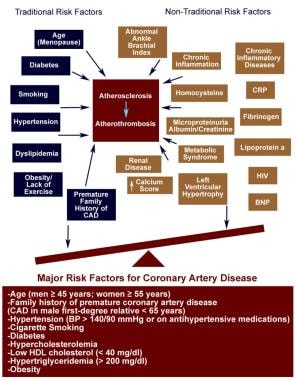
WHO World Health Organization Type 2 diabetes increases the risk of coronary heart disease CHD events at least by two- to threefold in type 2 diabetic subjects compared with nondiabetic subjects 1. Designation of a disorder as a coronary heart disease risk equivalent would imply that the disorder leads to a 10-year risk of coronary death or myocardial infarction that is at least as high as after myocardial infarction ie usually exceeding 201 Guidelines therefore recommend lipid-lowering therapy in addition to therapeutic lifestyle changes for most adults with a coronary heart disease risk. Coronary artery disease is the leading cause of death in the United States for both men and women.
Oronary heart disease CHD also called. 13 Of note a prior report based on Framingham risk.
The purpose of our study was to confirm or refute the view that diabetes be regarded as a coronary heart disease CHD risk equivalent and to test for sex differences in mortality.
Therefore CKD itself is now considered an independent CVD risk factor and a coronary artery disease CAD equivalent for all-cause mortality. The calculator reflects new guidelines and updates by the National Institutes of Health in December 2015. CHD occurs when plaque builds up inside the coronary arteries. Coronary heart disease equivalent. Treatments used for management of established CAD might have similar benefits for patients with concomitant CKD. WHO World Health Organization Type 2 diabetes increases the risk of coronary heart disease CHD events at least by two- to threefold in type 2 diabetic subjects compared with nondiabetic subjects 1. All patients at risk for CAD should be evaluated for kidney disease. 13 Of note a prior report based on Framingham risk. This implies important therapeutic psychological and economical consequences.
Furthermore they lend support for the 2013 American College of Cardiology ACCAmerican Heart Association AHA risk assessment guidelines inclusion of diabetes as a predictor rather than an automatic coronary heart disease risk equivalent and consideration of global risk assessment eg with the Pooled Cohort Risk Calculator to help discriminate those with DM who are at higher versus lower risk. For more than a decade the presence of diabetes has been considered a coronary heart disease CHD risk equivalent. This was a prospective cohort study of 7052 men and 8354 women aged 45-64 years from Renfrew and Paisley Scotland who were first screened in 1972-1976 and followed for 25. 13 Of note a prior report based on Framingham risk. The objective was to evaluate the odds of peripheral arterial disease PAD or carotid artery stenosis CAS among participants with diabetes CHD or both compared with participants without diabetes or CHD in a nationwide vascular. Furthermore they lend support for the 2013 American College of Cardiology ACCAmerican Heart Association AHA risk assessment guidelines inclusion of diabetes as a predictor rather than an automatic coronary heart disease risk equivalent and consideration of global risk assessment eg with the Pooled Cohort Risk Calculator to help discriminate those with DM who are at higher versus lower risk. The calculator reflects new guidelines and updates by the National Institutes of Health in December 2015.













32279-3.fp.png)






















Post a Comment for "Coronary Heart Disease Risk Equivalent"