Hyperphosphatemia Chronic Kidney Disease
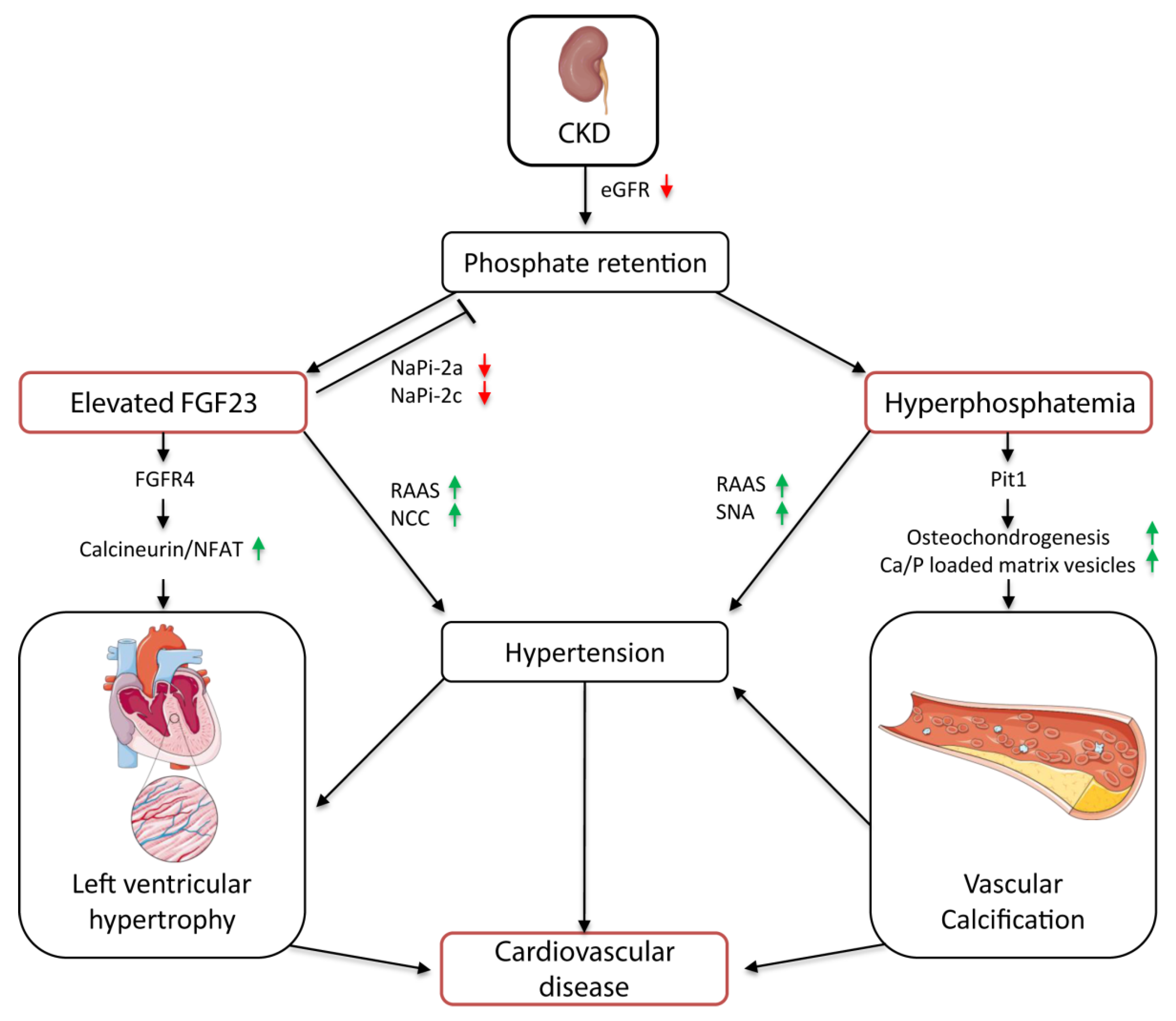
Hyperphosphatemia chronic kidney disease. Hyperphosphatemia is common in chronic kidney disease CKD. Hyperphosphatemia has consistently been shown to be associated with dismal outcome in a wide variety of populations particularly in chronic kidney disease CKD. Mechanistic studies have elucidated that hyperphosphatemia is a direct stimulus to vascular calcification which is one cause of morbid.
To be a cardiovascular risk factor in chronic kidney disease. Pathophysiology of Hyperphosphatemia in Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral Bone Disorder. Mechanistic studies have elucidated that hyperphosphatemia is a direct stimulus to vascular calcification which is one cause of morbid cardiovascular events contributing to the excess mortality of chronic kidney disease.
Patients with chronic kidney disease and the underlying mechanisms by which phosphate directly affects vessel lipid homeostasis without changing blood lipid levels. Protect your kidneys by treating the cause of your kidney disease. Observational studies have determined hyperphosphatemia to be a cardiovascular risk factor in chronic kidney disease.
Secondary hyperparathyroidism SHPT is associated with progression of chronic kidney disease CKD and possibly cardiovascular events independently of hyperphosphatemia a new. Observational studies have determined hyperphosphatemia to be a cardiovascular risk factor in chronic kidney disease. The hidden killer in chronic kidney disease.
Observational studies have determined hyperphosphatemia to be a cardiovascular risk factor in chronic kidney disease. Ramos1 Marta Albalate1 Silvia Vazquez2 Carlos Caramelo1 Jesus Egido1 and Alberto Ortiz1 1Nephrology and Hypertension Unit Jimenez Diaz Foundation-Capio Autonomous University of Madrid Madrid Spain and 2Statistical. Hyperphosphatemia is often a complication of chronic kidney disease.
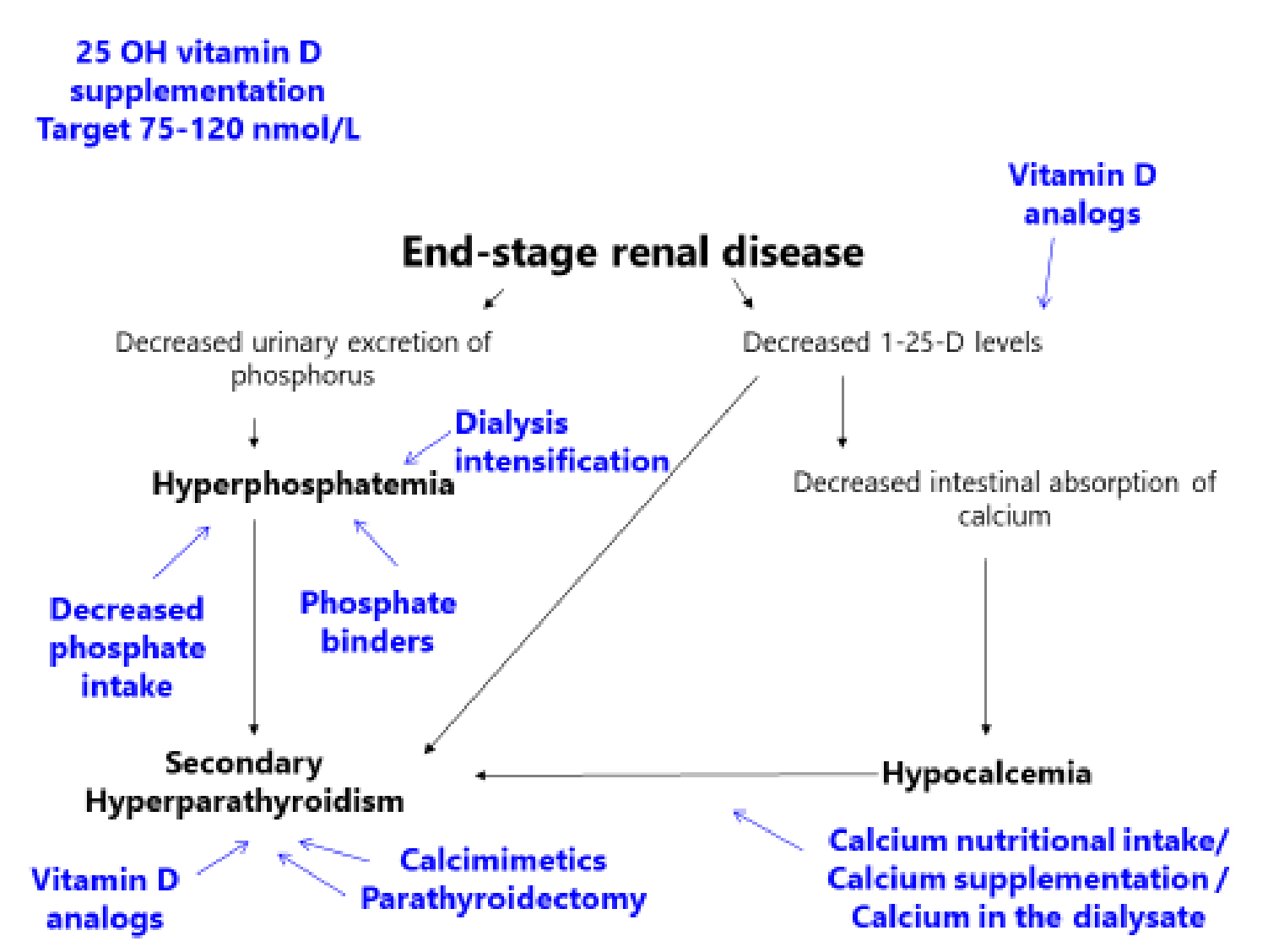
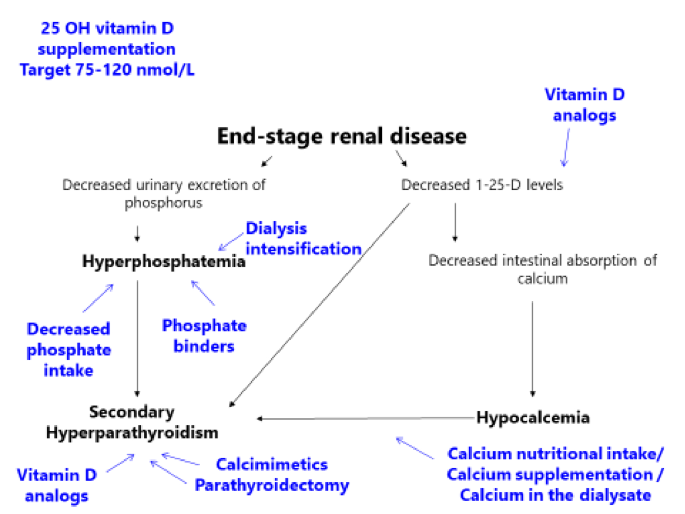
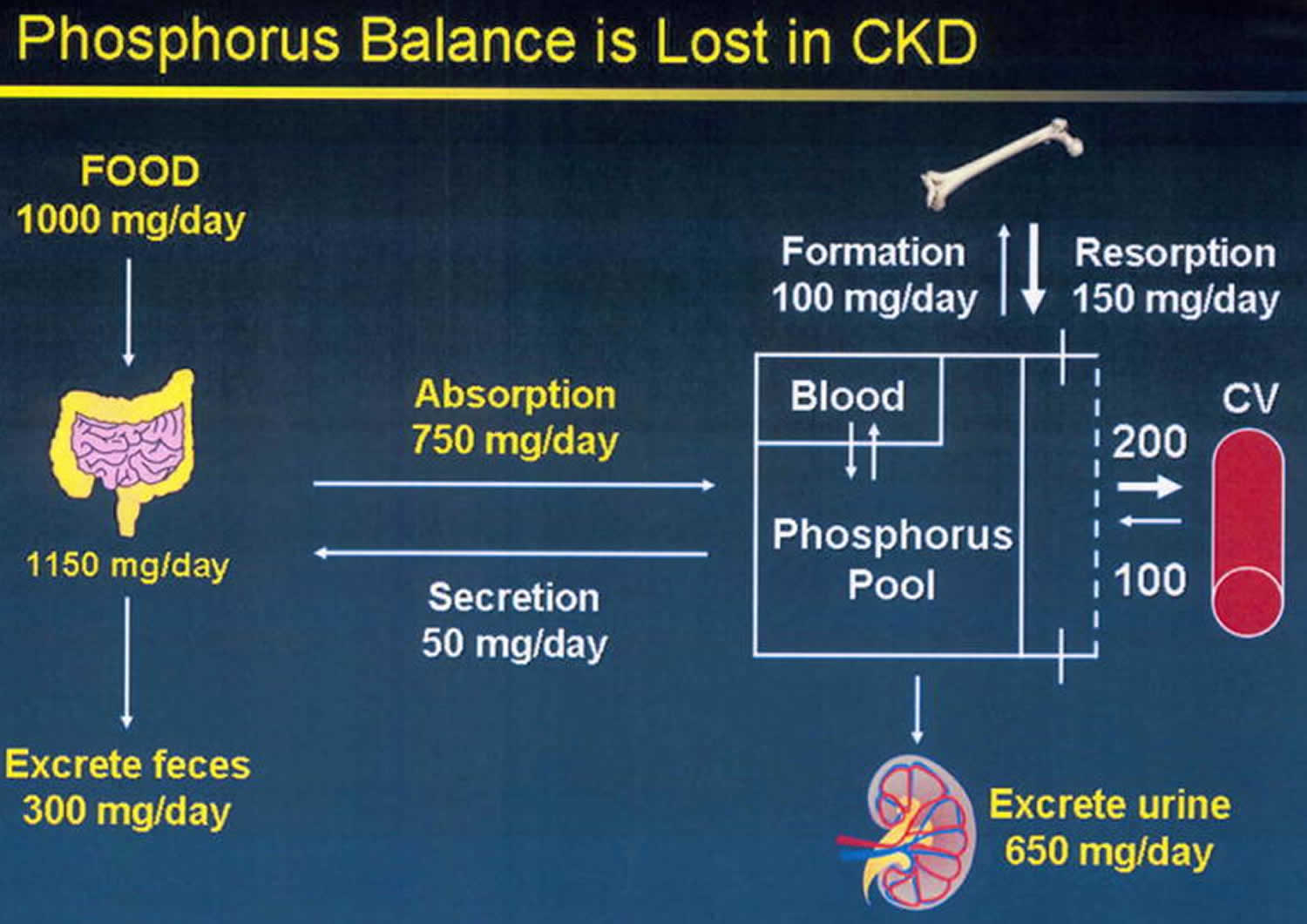
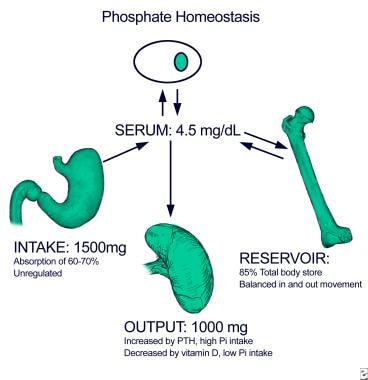
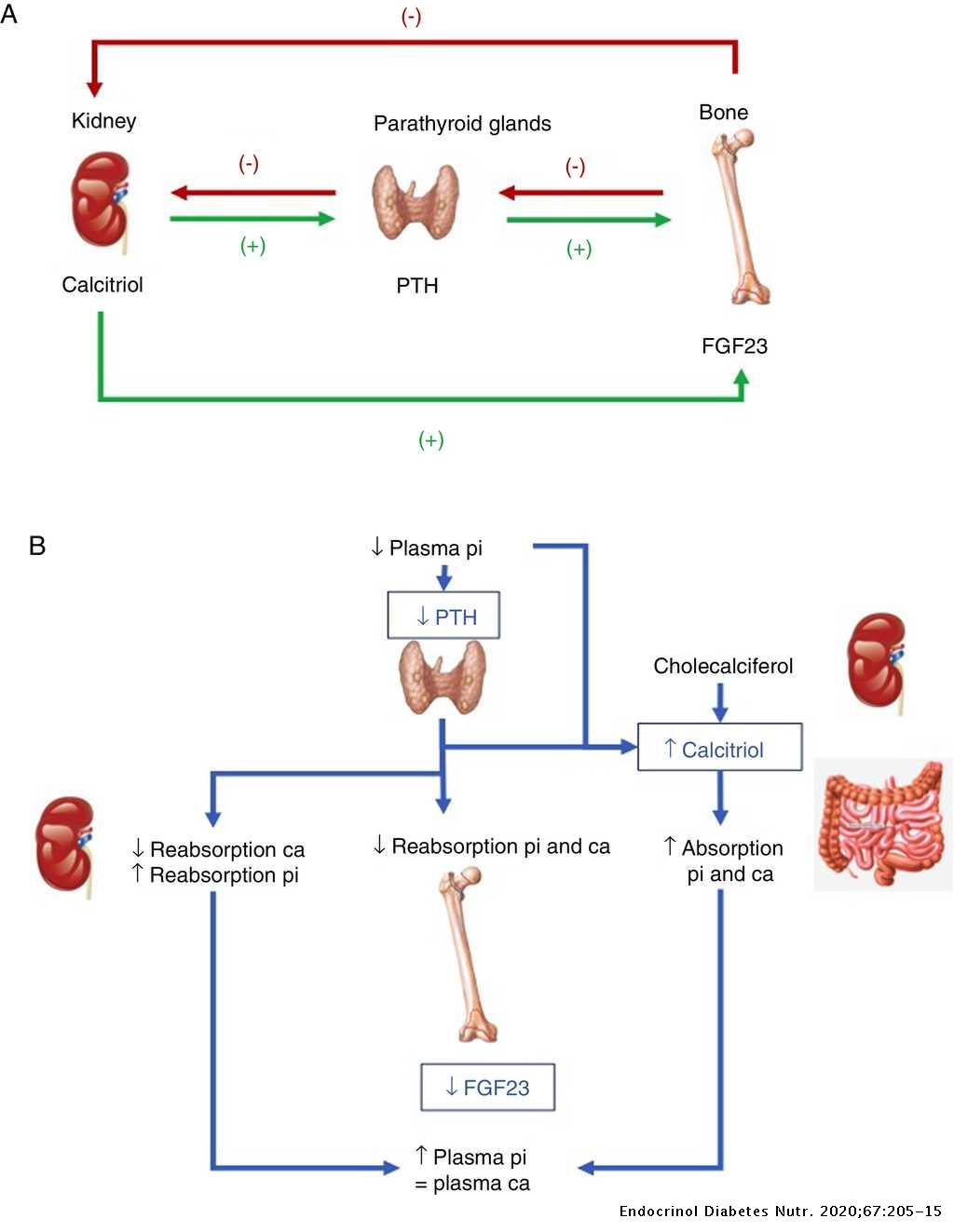
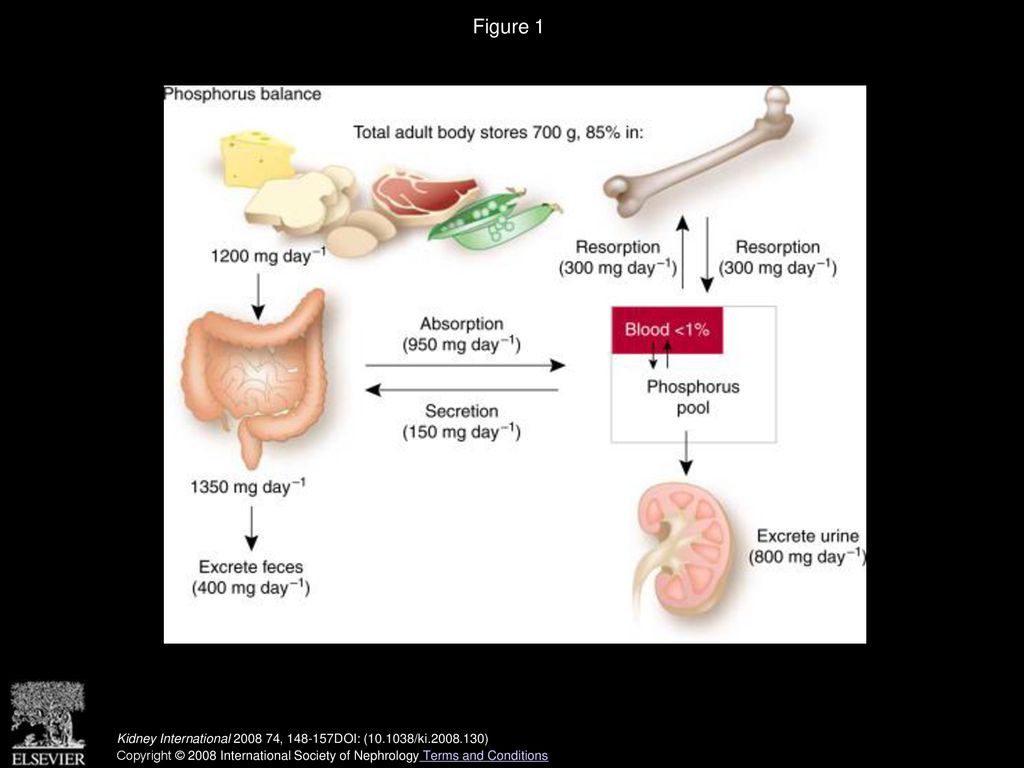
Serum phosphorus balance is dependent on the contribution of dietary phosphorus absorption in the intestine glomerular filtration and tubular excretion and reabsorption in the kidney and a balance between bone formation and resorption. 1 As the kidneys continue to lose function a decrease in vitamin D receptors and calcium-sensing receptors in the parathyroid glands occur. Hyperphosphatemia and hyperparathyroidism in incident chronic kidney disease patients Ana M.
Hyperphosphatemia accelerates atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease but the underlying mechanisms are still. Mechanistic studies have elucidated that hyperphosphatemia is a direct stimulus to vascular calcification which is one cause of morbid cardiovascular events contributing to the excess mortality of chronic kidney disease.
Pathophysiology of Hyperphosphatemia in Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral Bone Disorder.
1 As the kidneys continue to lose function a decrease in vitamin D receptors and calcium-sensing receptors in the parathyroid glands occur. To be a cardiovascular risk factor in chronic kidney disease. Mechanistic studies have elucidated that hyperphosphatemia is a direct stimulus to vascular calcification which is one cause of morbid cardiovascular events contributing to the excess. The association between hyperphosphatemia and increased risk of death from cardiovascular diseasevascular calcification has been well established for a long time. Ramos1 Marta Albalate1 Silvia Vazquez2 Carlos Caramelo1 Jesus Egido1 and Alberto Ortiz1 1Nephrology and Hypertension Unit Jimenez Diaz Foundation-Capio Autonomous University of Madrid Madrid Spain and 2Statistical. The hidden killer in chronic kidney disease. 1 As the kidneys continue to lose function a decrease in vitamin D receptors and calcium-sensing receptors in the parathyroid glands occur. Pathophysiology of Hyperphosphatemia in Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral Bone Disorder. Hyperphosphatemia is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease.
Hyperphosphatemia accelerates atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease but the underlying mechanisms are still. Hyperphosphatemia accelerates atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease but the underlying mechanisms are still. Patients with chronic kidney disease and the underlying mechanisms by which phosphate directly affects vessel lipid homeostasis without changing blood lipid levels. Mechanistic studies have elucidated that hyperphosphatemia is a direct stimulus to vascular calcification which is one cause of morbid. Hyperphosphatemia in chronic kidney disease exacerbates atherosclerosis via a mannosidases-mediated complex-type conversion of SCAP N-glycans Graphical abstract. Hyperphosphatemia of chronic kidney disease. Secondary hyperparathyroidism SHPT is associated with progression of chronic kidney disease CKD and possibly cardiovascular events independently of hyperphosphatemia a new.



































Post a Comment for "Hyperphosphatemia Chronic Kidney Disease"