Stage 3 Kidney Disease And Pregnancy
Stage 3 kidney disease and pregnancy. Chronic Kidney Disease and Pregnancy. The greatest risk is for mothers on dialysis. The higher the stage of CKD the greater the risk for both mother and baby.
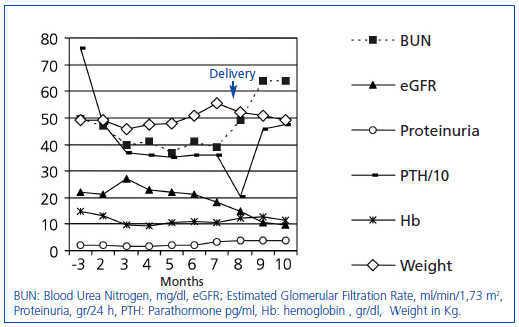
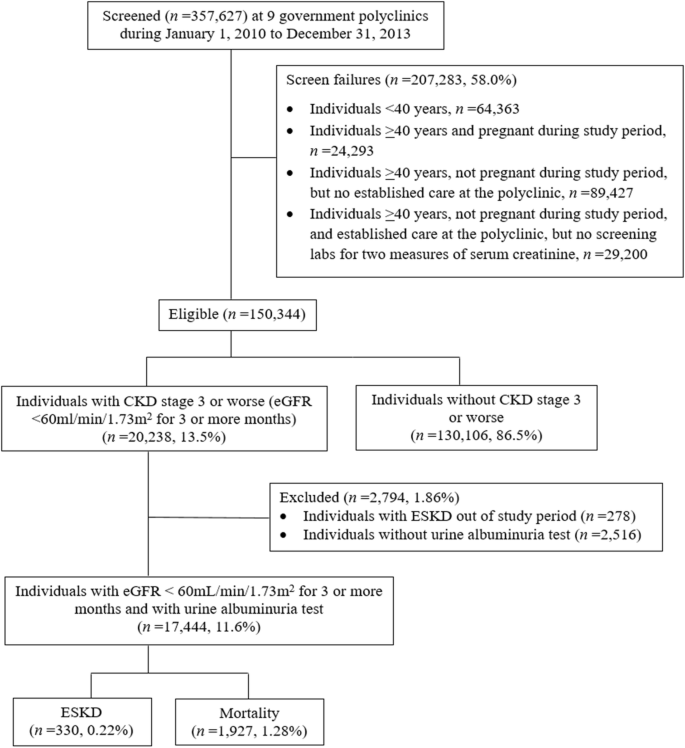
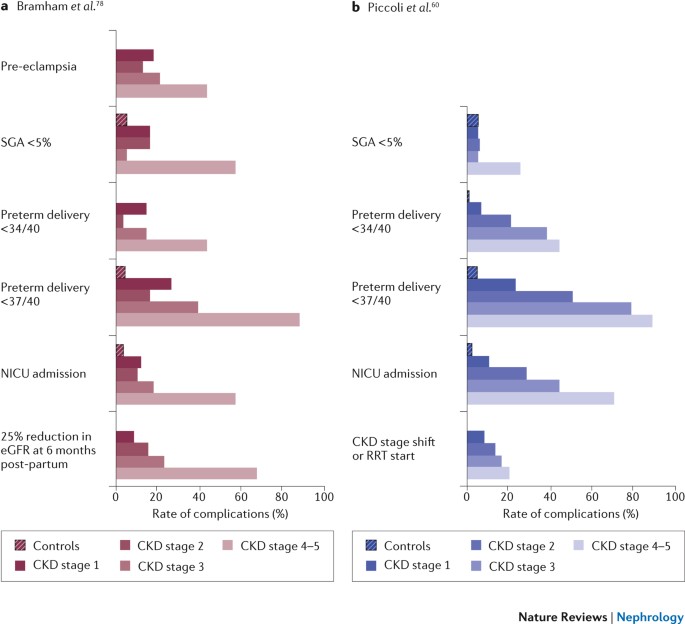
During the follow-up period 8 patients progressed to ESRD. With CKD stages 3 to 5 preg-nancy complication rates remain high Table 2. During the follow-up period 8 patients progressed to ESRD.
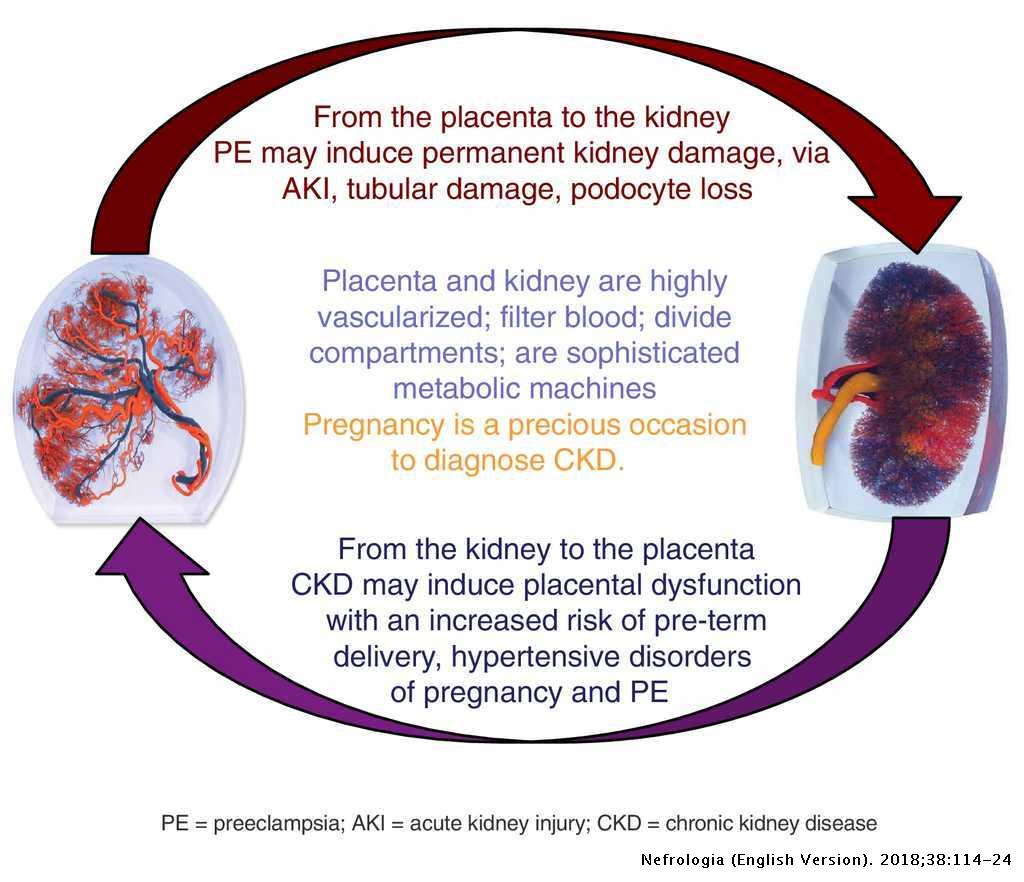
Half the babies will require special. Women with chronic kidney disease CKD are at risk for adverse pregnancy-associated outcomes including progression of their underlying renal dysfunction a flare of their kidney disease and adverse pregnancy complications such as preeclampsia and preterm delivery. Nevertheless CKD can have an impact on the health of pregnant women and there are potential risks for the baby.
The mean postpartum follow-up time of pregnant patients with CKD was 490331 months. W3 Stages 3-5 glomerular filtration rate. Decline in GFR without recovery 10.
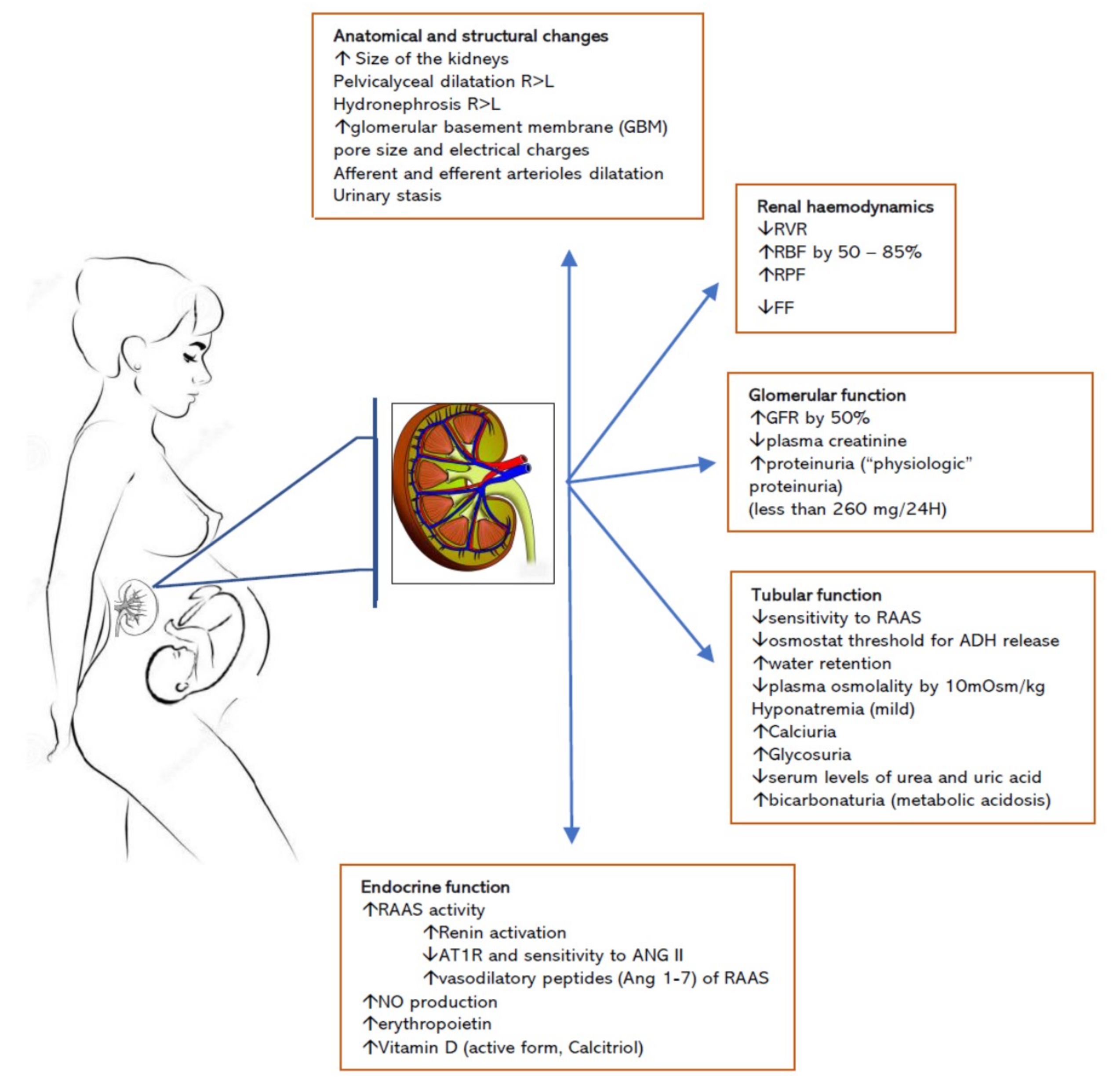
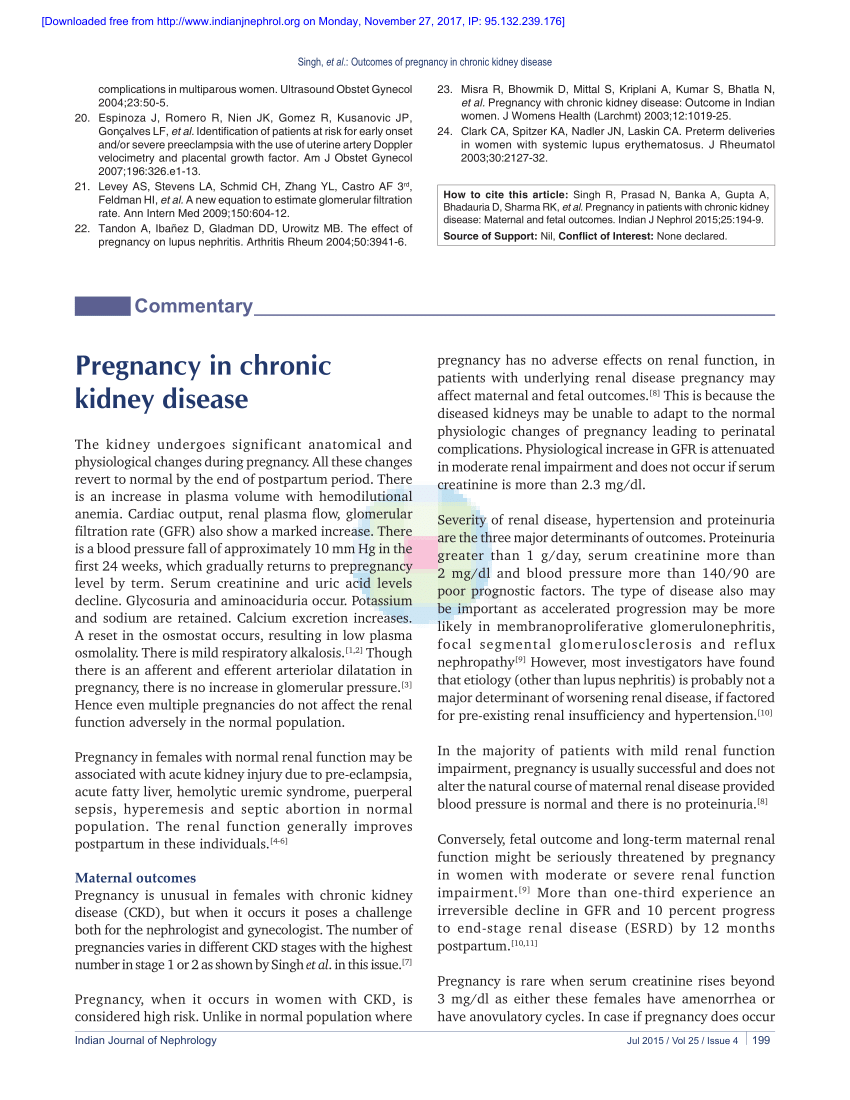
Pregnancy becomes increasingly challenging as young women progress through the stages of chronic kidney disease CKD. Earlier-stage CKD as a rule is. If you have existing kidney disease wed ideally like to see you prior to becoming pregnant to help optimize your health.
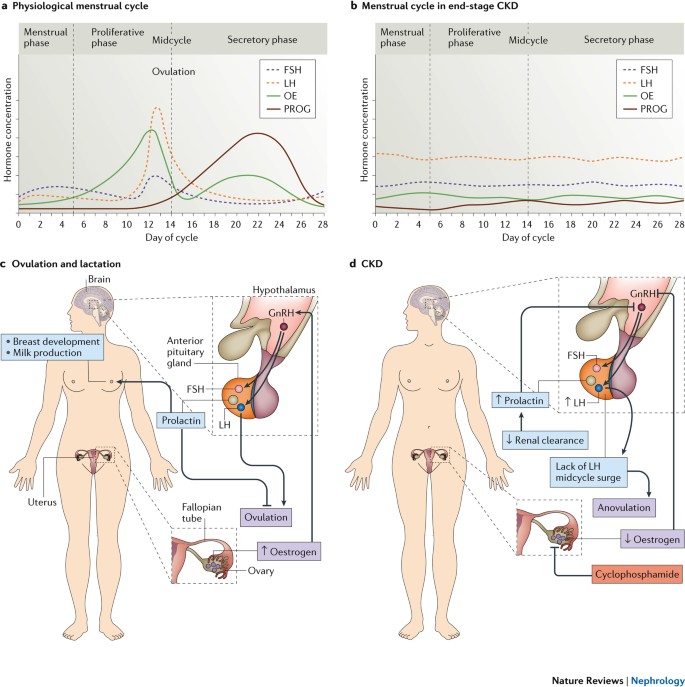
Women with advanced chronic kidney disease CKD have a lower likelihood of conceiving because of the decreased fertility associated with the hormonal changes of worsening kidney function and end-stage renal disease ESRD. Decline in GFR between 6 weeks and 6 months PP Cr 14 19 1 in 49 2 have worsening of renal disease. Keywords Chronic kidney disease Pregnancy Renal disease progression Introduction.
The incidence of adverse pregnancy outcomes of patients with stage 34 CKD was significantly higher than that with stage 1 CKD. Potential untoward outcomes include the progression of underlying renal dysfunction worsening of urine protein and hypertension as well as untoward fetal outcomes including intrauterine growth restriction and preterm delivery.
How common is chronic kidney disease in pregnancy.
On the other hand if you have a kidney disease that flares up and then settles down such as lupus nephritis it is better to wait until the flare has settled for at least six months. On the other hand if you have a kidney disease that flares up and then settles down such as lupus nephritis it is better to wait until the flare has settled for at least six months. The incidence of adverse pregnancy outcomes of patients with stage 34 CKD was significantly higher than that with stage 1 CKD. W3 Stages 3-5 glomerular filtration rate. Kidney disease prior to pregnancy. Potential untoward outcomes include the progression of underlying renal dysfunction worsening of urine protein and hypertension as well as untoward fetal outcomes including intrauterine growth restriction and preterm delivery. Chronic Kidney Disease and Pregnancy. Conditions that affect the kidneys are associated with an increased risk of fetal complications such as preterm birth and pregnancy loss. The incidence of adverse pregnancy outcomes of patients with stage 3-4 CKD was significantly higher than that with stage 1 CKD.
Conclusion Patients with stage 34 CKD in early pregnancy had a significantly increased risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes. For some women the risk to mother and child is high enough that they should consider avoiding pregnancy. Nevertheless CKD can have an impact on the health of pregnant women and there are potential risks for the baby. Pregnancy itself did not seem to accelerate kidney disease progression in patients with stage 34 CKD. The mean postpartum follow-up time of pregnant patients with CKD was 490331 months. The greatest risk is for mothers on dialysis. Reliable data for rates of first-trimester miscarriage are not available but they are certainly higher than for healthy mothers.





























Post a Comment for "Stage 3 Kidney Disease And Pregnancy"