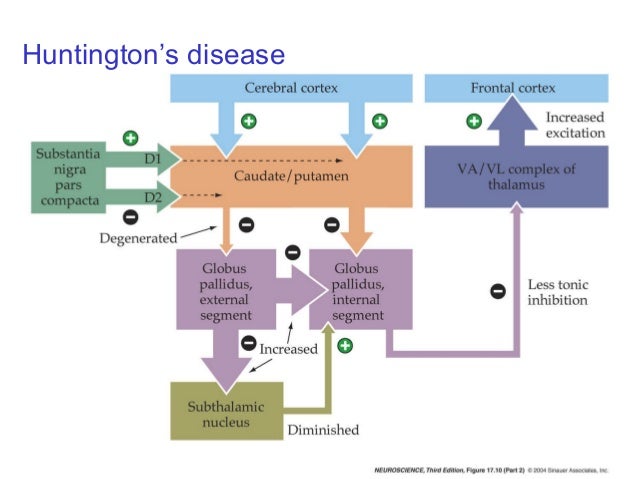
Huntington's Disease Basal Ganglia Pathway
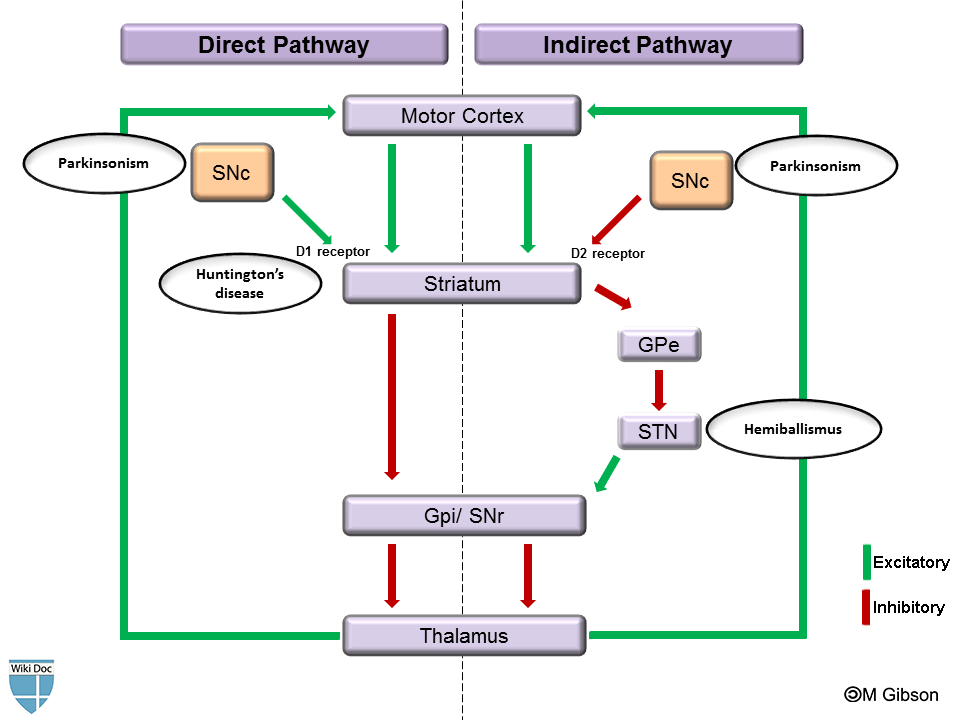
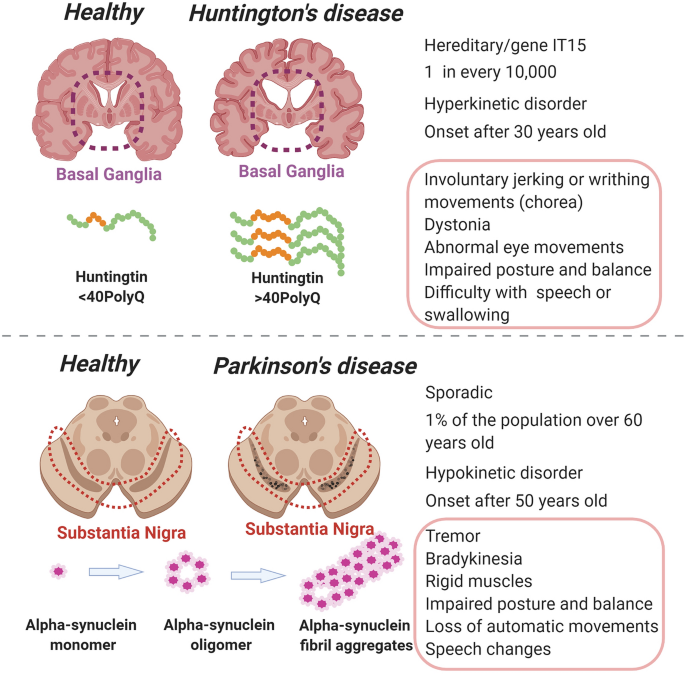
Huntington's disease basal ganglia pathway. Basal Ganglia in Huntingtons Disease Calgary Guide. The psychomotor symptoms of Huntingtons disease HD are linked to degeneration of the basal ganglia indirect pathway. This autosomal-dominant inherited disease is caused by mutations increased number of CAG trinucleotide repeats in the huntingtin gene which eventually leads to the dysfunction of subcortical motor circuits.
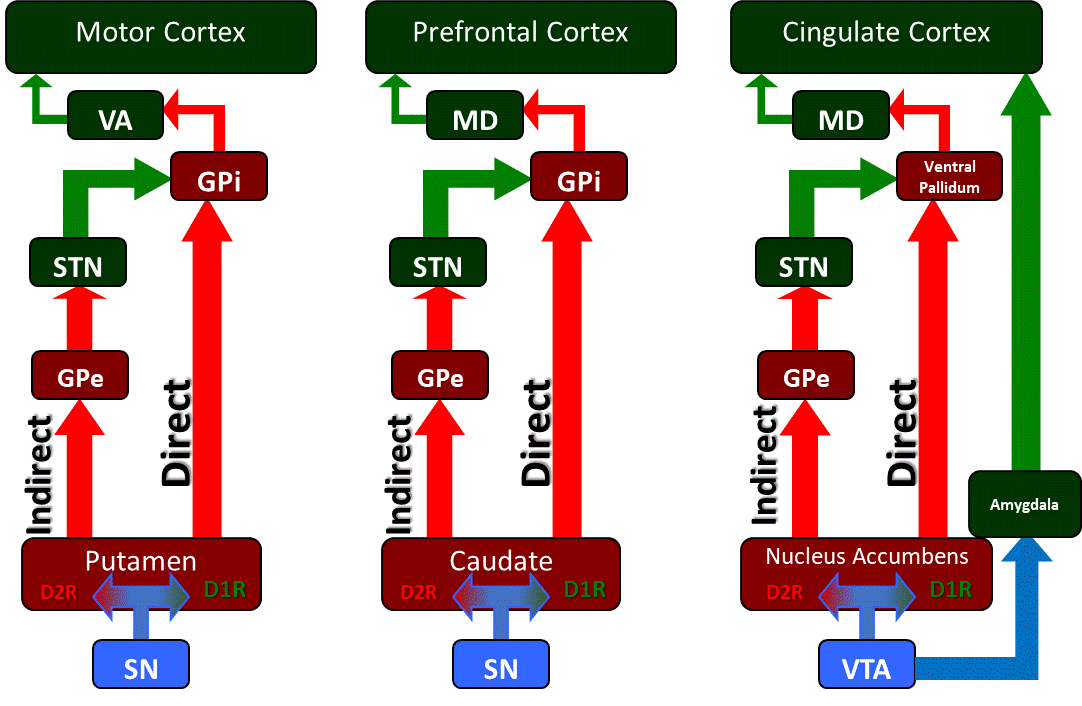
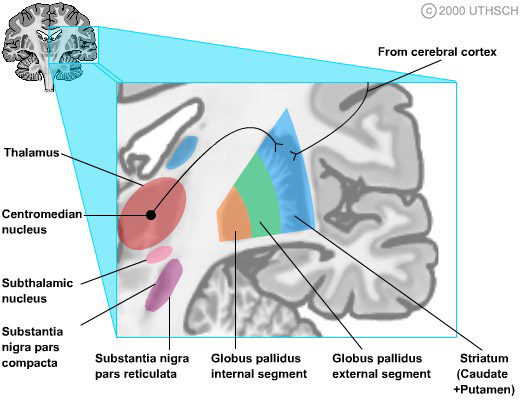
These give rise to two pathways that connect the striatum to the output nuclei of the basal ganglia namely globus pallidus pars interna GPi and the substantia nigra pars reticulata SNr. Basal ganglia circuits affect movements of the. Huntingtons disease HD is a hereditary neurodegenerative disease of the basal ganglia that causes severe motor cognitive and emotional dysfunctions.
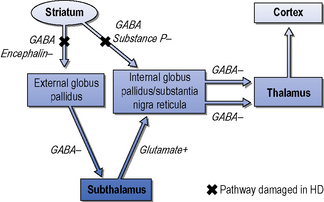
In the basal ganglia the progressive loss of striatal projection neurons combined with the slow atrophy of other nuclei were considered as the main neuropathological hallmarks of Huntingtons disease. Huntingtons disease HD is characterized by pronounced pathology of the basal ganglia with numerous studies documenting the pattern of striatal neurodegeneration in the human brain. In the human basal ganglia these dysfunctions are accompanied by a loss of striatal medium spiny neurons dysfunctions of the subthalamic nucleus and globus pallidus and changes in dopamine receptor binding.
Basal Ganglia Diseases Huntington Disease Dystonia Echogenic Bowel Velopharyngeal Insufficiency Urinary Bladder Neurogenic Urinary Bladder. Huntington Disease HD is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disorder with onset in middle age. An overview of the basal ganglia and the direct and indirect pathways model as well as how this applies to Parkinsons disease and Huntingtons disease as w.
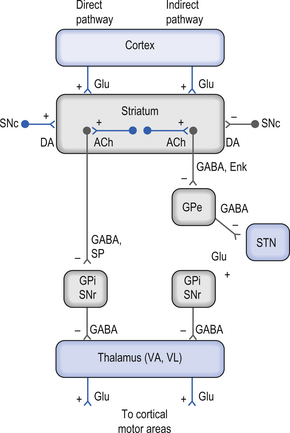
Thus the basal ganglia affect function mediated by the ipsilateral motor cortex. Three major pathways emerge from the basal ganglia which project onto various structures of the brain communicating with them. Huntingtons Disease and the Basal Ganglia Elizabeth Camarena St.
The understanding of the functional and structural changes occurring in the cerebral cortex and basal ganglia in Huntingtons disease HD has benefited considerably from the generation of genetic animal models. Dominic Savio High School Austin TX 78717 US BioScience Project Wakefield MA 01880 Huntingtons Disease is a genetic disease that breaks down the nerves in the brain. Symptoms of the disease can appear in ages 30 to 50 and it will affect a persons ability to.
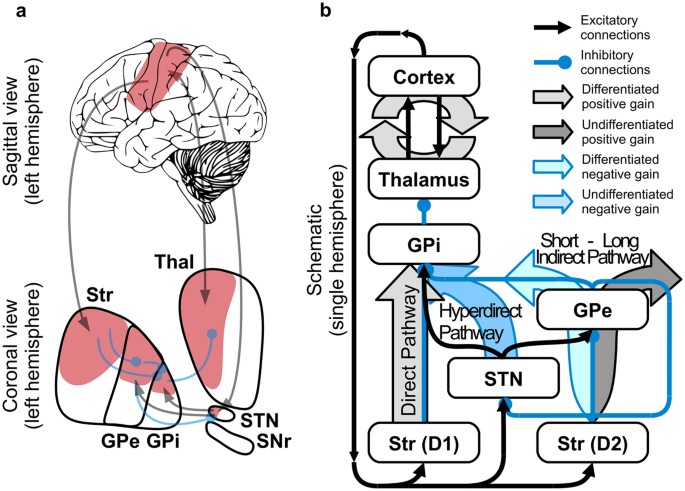
To determine how this pathway is perturbed prior to cell loss optogenetic- and reporter-guided electrophysiological interrogation approaches were applied to early symptomatic 6-month-old Q175 HD mice. It is characterized by atrophy of the basal ganglias caudate nucleus and manifests with involuntary choreiform movements as well as progressive dementia.
Basal Ganglia Caudate Nucleus Substantia Nigra Nerve Fibers Myelinated Neural Pathways Urinary Bladder Peripheral Nervous System.
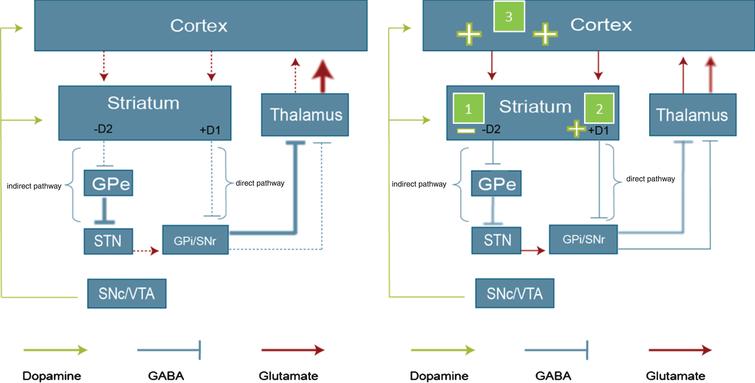
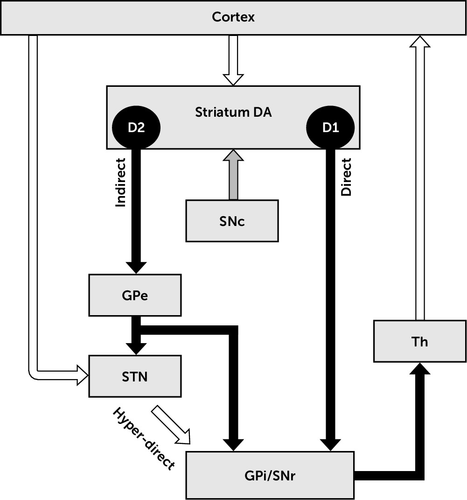
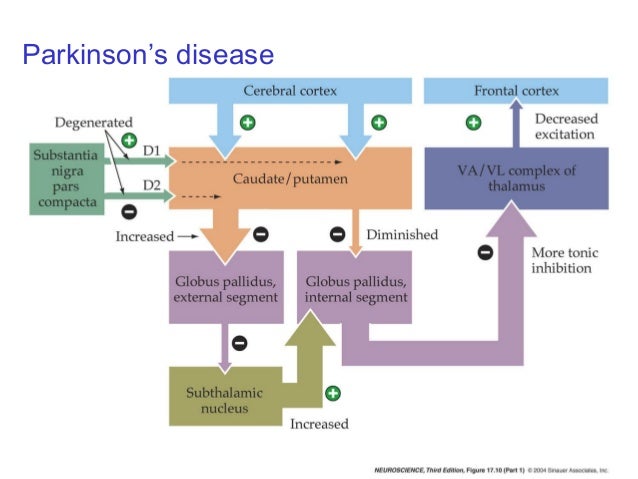
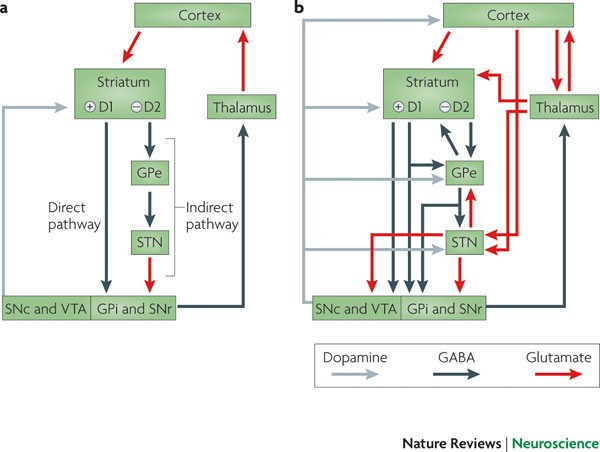
In the basal ganglia the progressive loss of striatal projection neurons combined with the slow atrophy of other nuclei were considered as the main neuropathological hallmarks of Huntingtons disease. They are called the direct excitatory indirect inhibitory and hyperdirect inhibitory pathways. Basal Ganglia Caudate Nucleus Substantia Nigra Nerve Fibers Myelinated Neural Pathways Urinary Bladder Peripheral Nervous System. To determine how this pathway is perturbed prior to cell loss optogenetic- and reporter-guided electrophysiological interrogation approaches were applied to early symptomatic 6-month-old Q175 HD mice. Parkinsons disease and Huntingtons disease are progressive neurodegenerative disorders of the basal ganglia and its connections that profoundly impact motor cognitive and psychiatric functions of affected individuals. These give rise to two pathways that connect the striatum to the output nuclei of the basal ganglia namely globus pallidus pars interna GPi and the substantia nigra pars reticulata SNr. Huntingtons disease HD is characterized by pronounced pathology of the basal ganglia with numerous studies documenting the pattern of striatal neurodegeneration in the human brain. Basal ganglia circuits affect movements of the. Since motor cortex controls the movements of the contralateral body.
Neurons in the direct pathway project directly from the putamen to GPiSNr. Most studies of synaptic alterations in HD models have focused on the striatum but a mo. An overview of the basal ganglia and the direct and indirect pathways model as well as how this applies to Parkinsons disease and Huntingtons disease as w. It is characterized by atrophy of the basal ganglias caudate nucleus and manifests with involuntary choreiform movements as well as progressive dementia. In the basal ganglia the progressive loss of striatal projection neurons combined with the slow atrophy of other nuclei were considered as the main neuropathological hallmarks of Huntingtons disease. Huntingtons Disease and the Basal Ganglia Elizabeth Camarena St. These give rise to two pathways that connect the striatum to the output nuclei of the basal ganglia namely globus pallidus pars interna GPi and the substantia nigra pars reticulata SNr.






















:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13859/Connections_of_basal_ganglia_-_hyperdirect_pathway.png)








Post a Comment for "Huntington's Disease Basal Ganglia Pathway"